AWS S3 Same Region Replication (SRR)
A step-by-step guide to configuring Amazon S3 Same Region Replication rule
Table of contents
- What is AWS S3 Same Region Replication (SRR)?
- Use Cases of AWS S3 Same Region Replication (SRR)
- What are the prerequisites to replicate S3 objects?
- What is replicated with the AWS S3 replication configuration rule?
- Which S3 objects are not replicated with Replication Configuration?
- Steps to configure the AWS S3 Same Region Replication
- AWS S3 Same Region Replication Pricing
- Conclusion
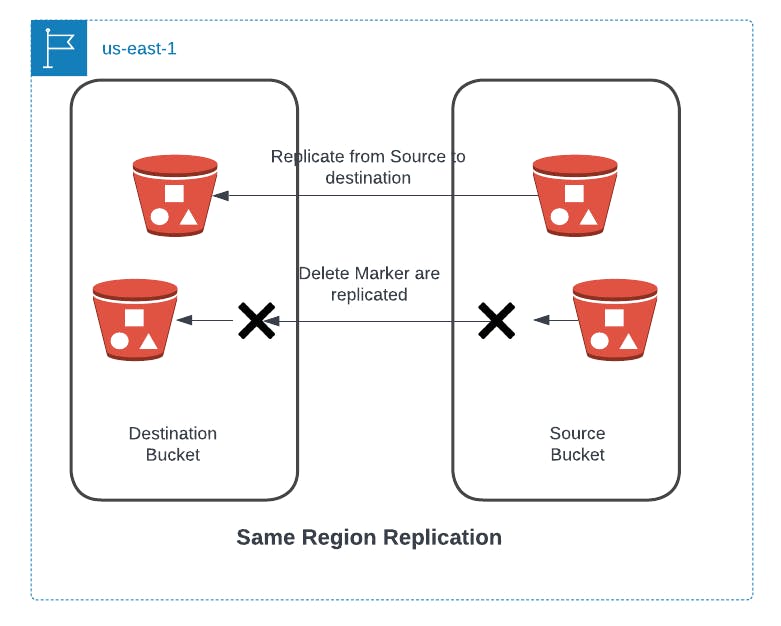
What is AWS S3 Same Region Replication (SRR)?
AWS S3 Same Region Replication allows replicating the newly uploaded objects to S3 destination buckets asynchronously and automatically present in the same region as the source bucket. Still, it could be in a different Availability Zone.
Users can configure the replication rule so the rule can identify the objects to replicate using prefix, tag, or bucket through AWS CLI, Management Console, and AWS SDK.
Also, users can configure to replicate S3 objects across cross-account in a single region or across cross region.
AWS S3 Cross Account Replication and AWS S3 Cross Region Replication we will cover in upcoming tutorials
Use Cases of AWS S3 Same Region Replication (SRR)
- When the user wants to ensure a replica of their objects for data compliance requirements
- The user wants to update the ownership of objects to protect against accidental data deletion.
- You can configure the in-Region replication to aggregate the logs from multiple S3 buckets to a single S3 bucket for more explicit processing.
- When the user wants to change their objects' storage class, you can use the S3 object lifecycle.
- The user wants to configure live data replication between multiple accounts, such as Stage and Production accounts.
What are the prerequisites to replicate S3 objects?
- User must enable versioning at S3 source and destination bucket
- Proper IAM policies and bucket policies must be created to give AWS S3 Permission to replicate the objects on the user's behalf
- If the source bucket has object lock enabled, the destination bucket also must have enabled the same
What is replicated with the AWS S3 replication configuration rule?
- The objects uploaded after you create the replication configuration are replicated automatically. In addition, you can use the AWS S3 Replication Batch job to replicate existing objects.
- Object's metadata from the source object to the replicas
- Only objects in the source bucket for which the bucket owner has permissions to read objects and access control lists (ACLs)
- Object tags and S3 Object Lock retention information, if any
Which S3 objects are not replicated with Replication Configuration?
- Already replicated objects present in the bucket has the status "REPLICA."
- Objects in the source bucket have already been replicated to a different destination. So, for example, if you change the destination bucket in an existing replication configuration, Amazon S3 won't replicate the objects again.
- Objects in the source bucket that the bucket owner doesn't have sufficient permissions to replicate Actions performed by the bucket's lifecycle configuration
Steps to configure the AWS S3 Same Region Replication
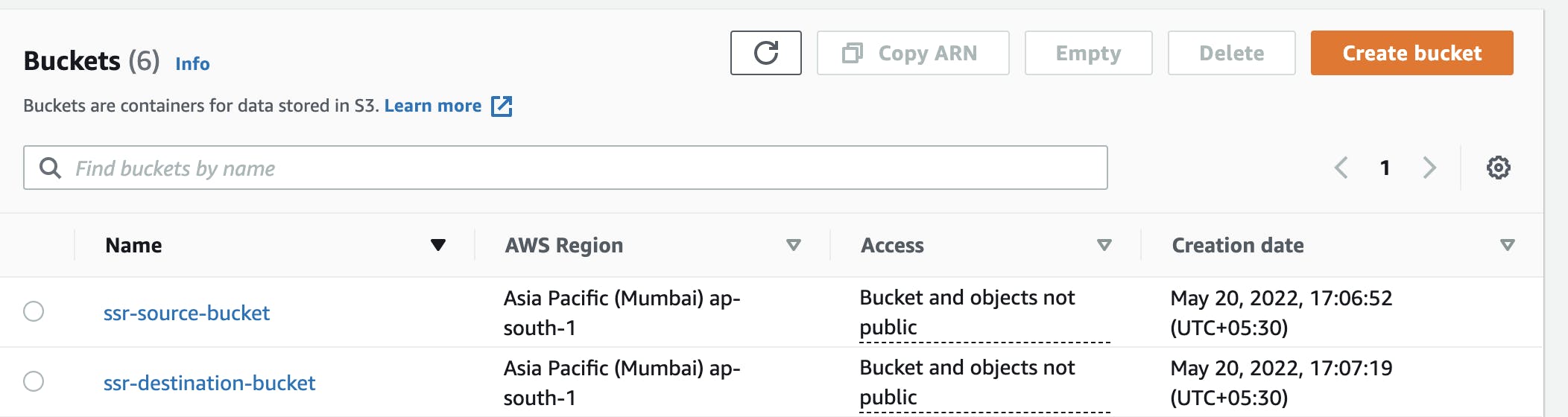
a. Create an S3 Source and Destination Buckets
- Create an S3 source bucket and an S3 destination bucket in your AWS Management Console in the same AWS Region.
- Make sure your bucket's name is unique and DNS compatible; you must enable bucket versioning while creating buckets.
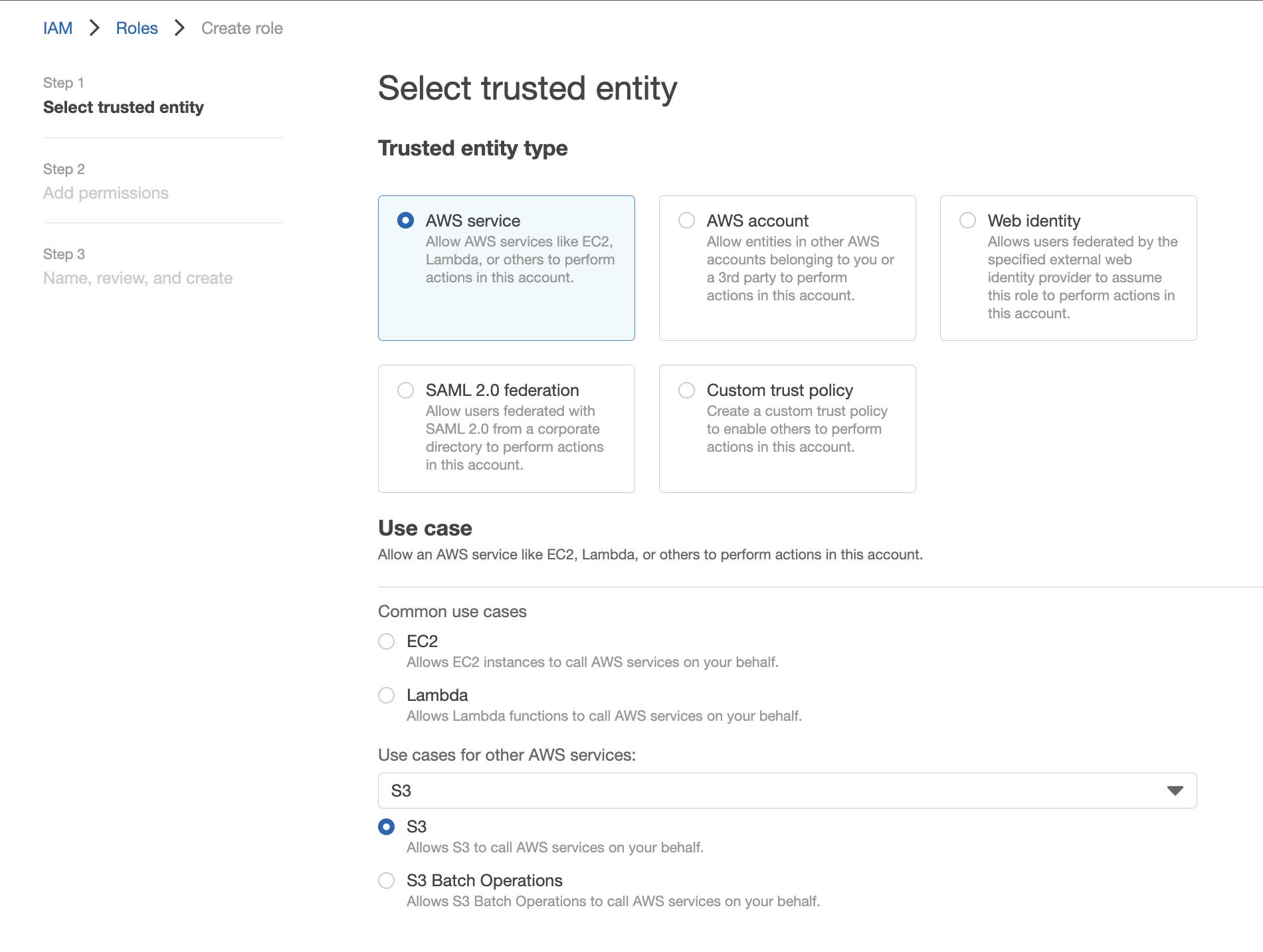
b. Set up an AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) role and policy
- User must create a role using which Amazon S3 can assume to replicate objects on the user's behalf
- Go to IAM Console and select Roles from the left navigation under Access Management.
- Choose to create a role from Role Dashboard, select AWS Service as a trusted Entity, and choose S3 from the bottom dropdown for Use Case and press Next.
- At Permission, choose Create Policy and select JSON tab, and copy-paste below policy code.
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"s3:GetReplicationConfiguration",
"s3:ListBucket"
],
"Resource": [
"arn:aws:s3:::<source-bucket>"
]
},
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"s3:GetObjectVersionForReplication",
"s3:GetObjectVersionAcl",
"s3:GetObjectVersionTagging"
],
"Resource": [
"arn:aws:s3:::<source-bucket>/*"
]
},
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"s3:ReplicateObject",
"s3:ReplicateDelete",
"s3:ReplicateTags"
],
"Resource": "arn:aws:s3:::<destination-bucket>/*"
}
]
}
- Replace the source bucket and destination bucket name according to your respective name
- The access policy grants the below permissions
- s3:GetReplicationConfiguration and s3:ListBucket: It allows S3 to get information on replication configuration and buckets on the source bucket
- s3:GetObjectVersionForReplication and s3:GetObjectVersionAcl: This Permission allows Amazon S3 to get a specific object version and access control list (ACL) associated with the objects.
s3:ReplicateObject and s3:ReplicateDelete: This Permission allows Amazon S3 to replicate objects or delete markers to the destination bucket
Click on Tags, add tags if you want to, and Press Next.
- Name the policy and click on Create policy.
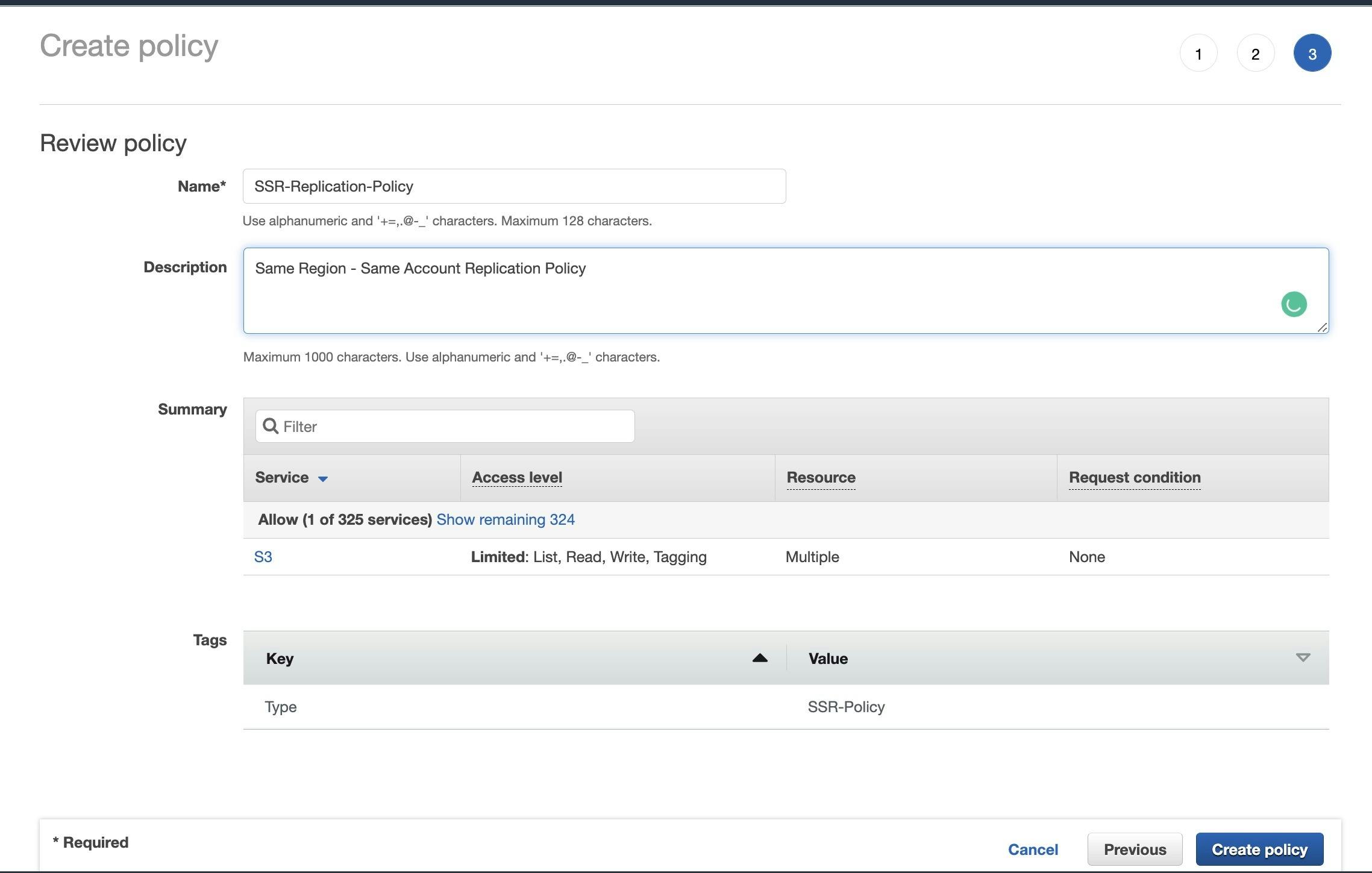
- On Add Permission page, refresh at Permission policies. You can see your new policy created listed. Select your policy and press Next.
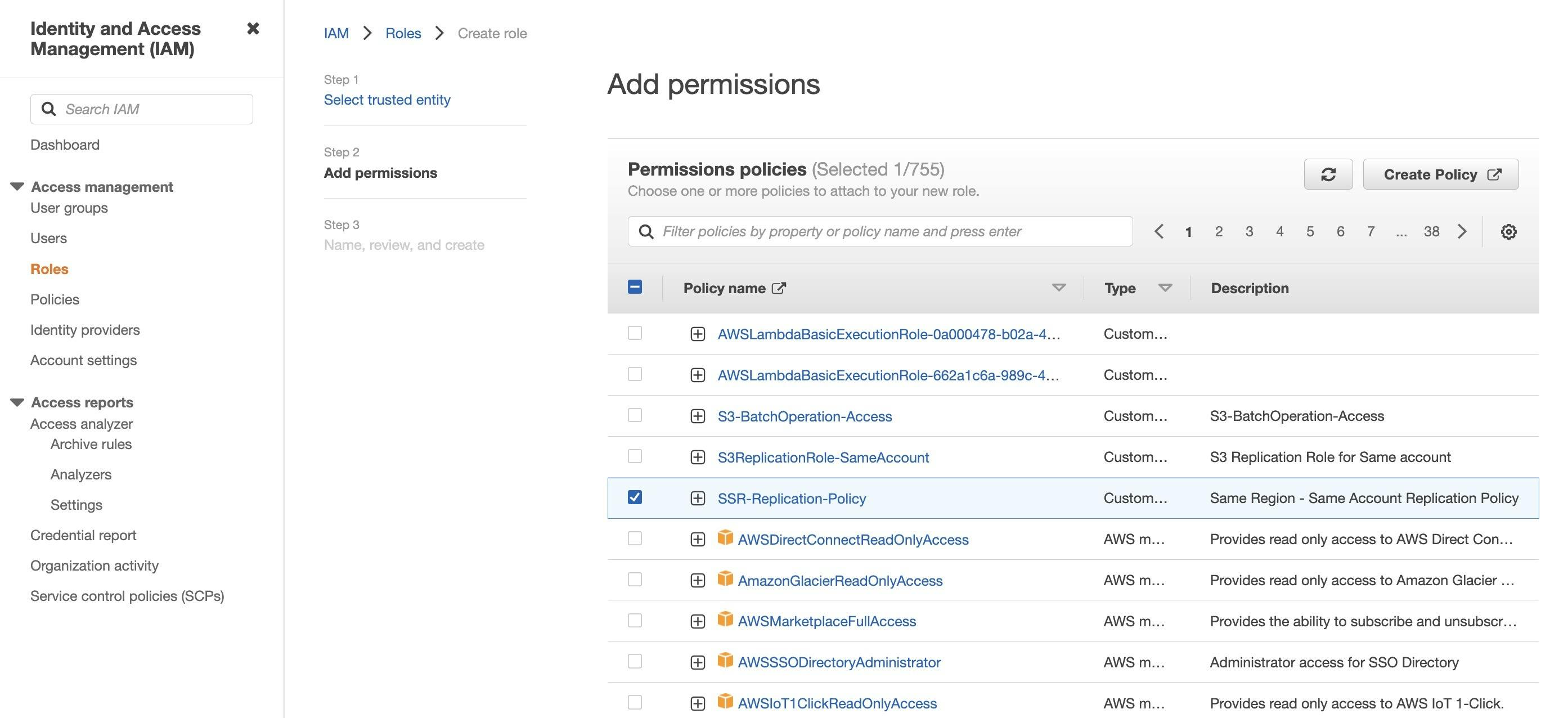
- Name your role and description, and press Create Role.
c. Create Replication Configuration Rule
- Open the S3 console, console.aws.amazon.com/s3
- Select your source bucket, choose the Management tab, and scroll down to Replication Rules. Click on Create Replication Rule
-
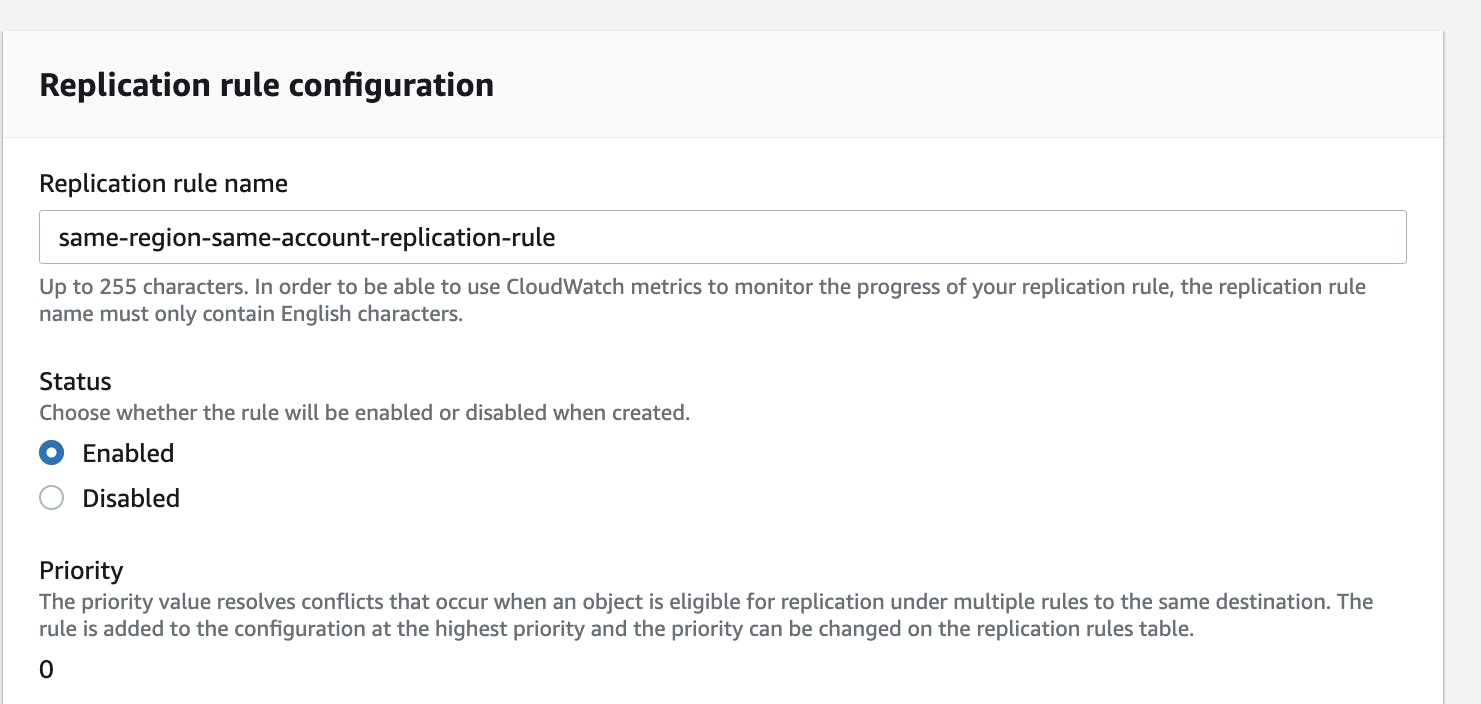
Provide Replication Rule Name
-
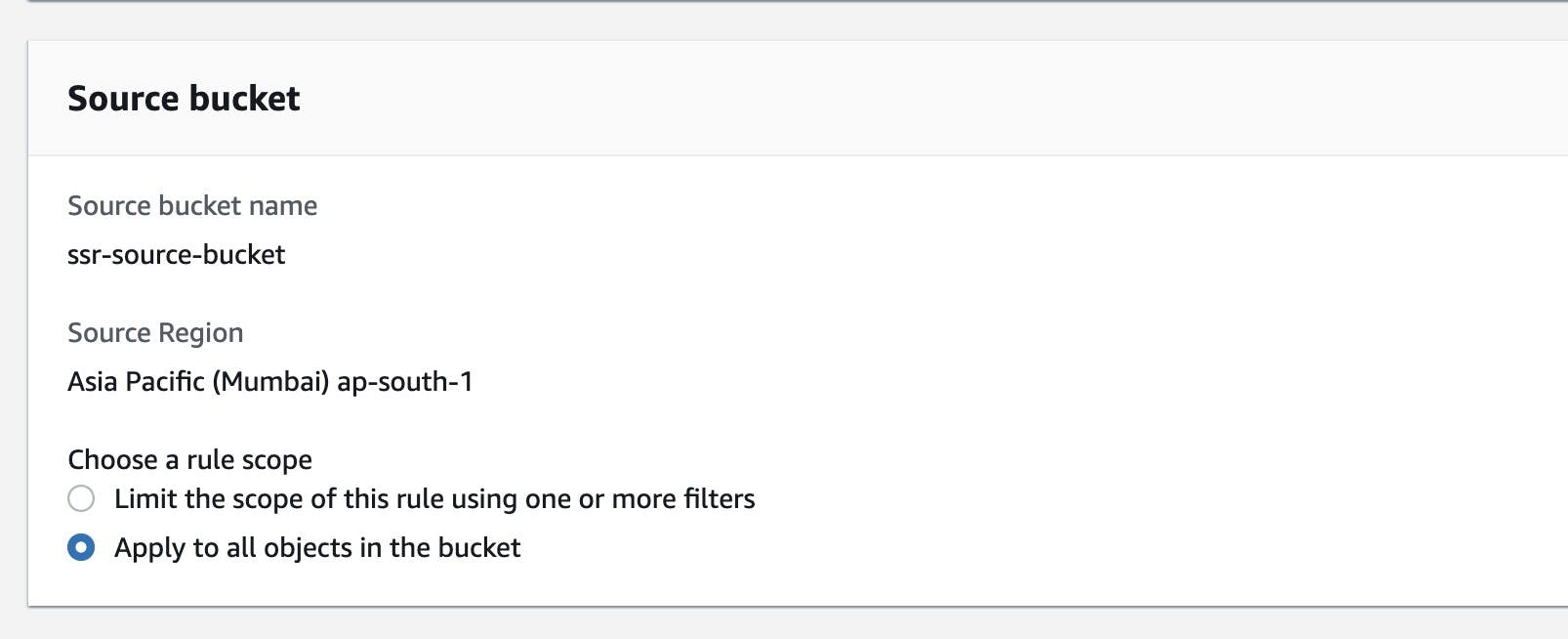
Under Source Bucket
- You can provide the prefix of objects you want to replicate
- We will select "Apply to all objects in the bucket" for this tutorial.
-
Under Destination Bucket
- Select "Choose a bucket in this account" and press browse S3 to get the bucket list.
- Select your destination bucket and click on Choose Path.
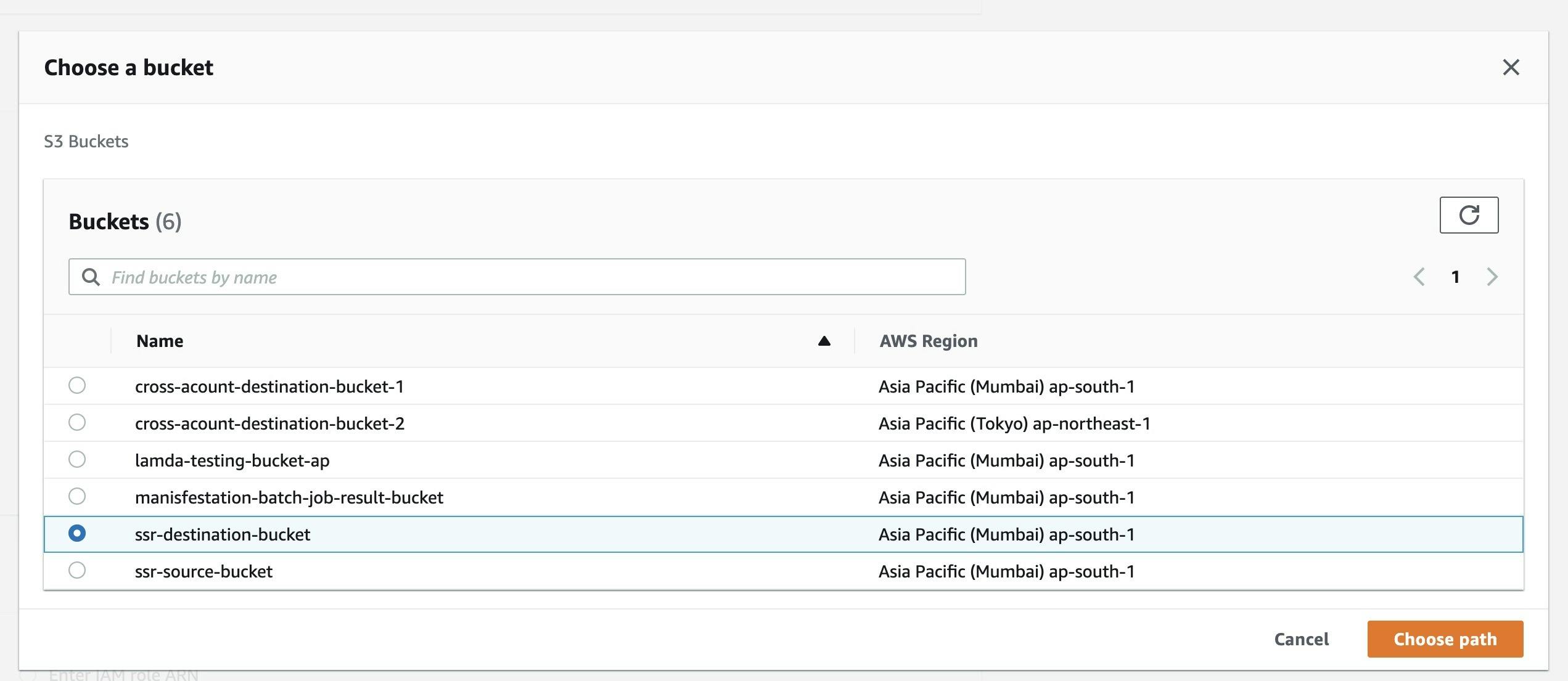
-
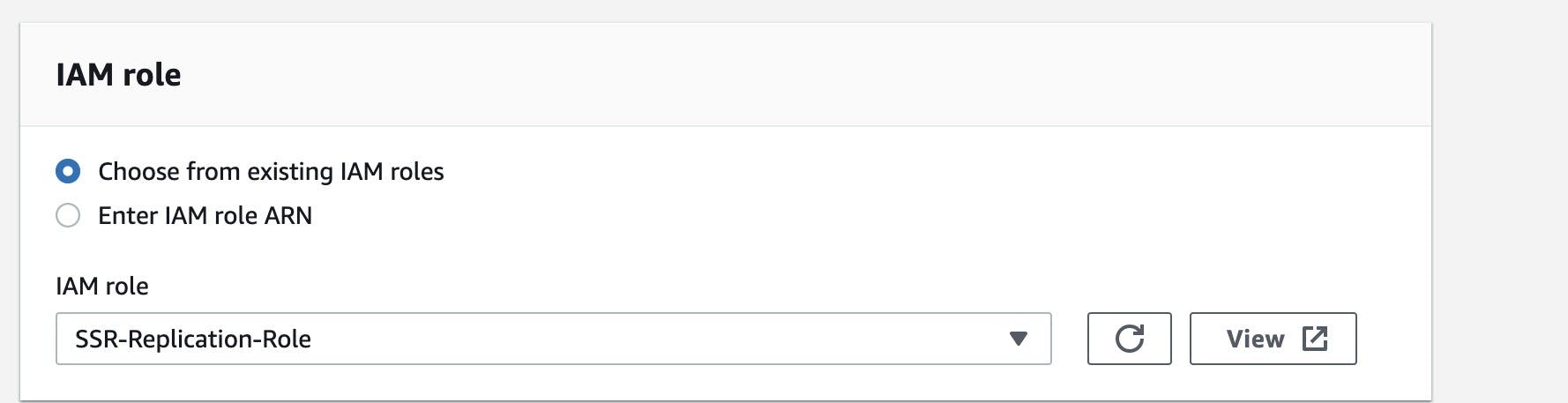
Under IAM Role
- Select "Choose from existing IAM roles" and select role created earlier.
- Under Destination Storage Class, you have an option to change the storage class of replicating objects. For this tutorial, let's keep the storage class the same as the source bucket.
-
Additional replication options
- Replication Time Control (RTC) - S3 Replication Time Control (S3 RTC) helps you meet compliance or business requirements for data replication and provides visibility into Amazon S3 replication times. S3 RTC replicates most objects you upload to Amazon S3 in seconds and 99.99 percent of those objects within 15 minutes..
- Delete marker replication - AWS S3 allows you to replicate the delete marker to your destination buckets. Amazon S3 behaves as if the object was deleted in both source and destination buckets.
- Replica modification sync - Amazon S3 replica modification sync can help you keep object metadata such as tags, ACLs, and Object Lock settings replicated between replicas and source objects. When replica modification sync is enabled, Amazon S3 replicates metadata changes made to the replica copies back to the source object, making the replication bidirectional.
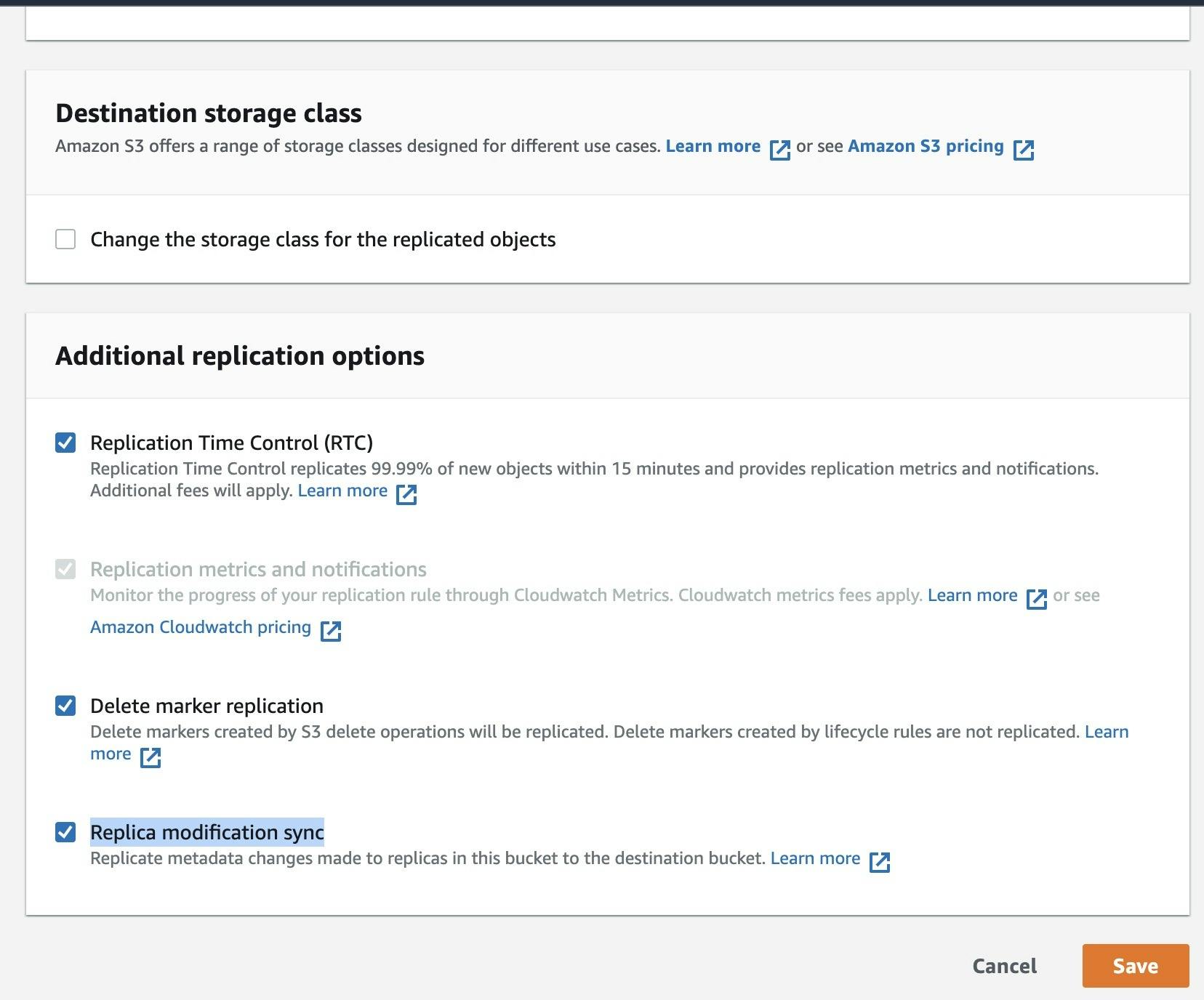
- Press Save to create your replication rule
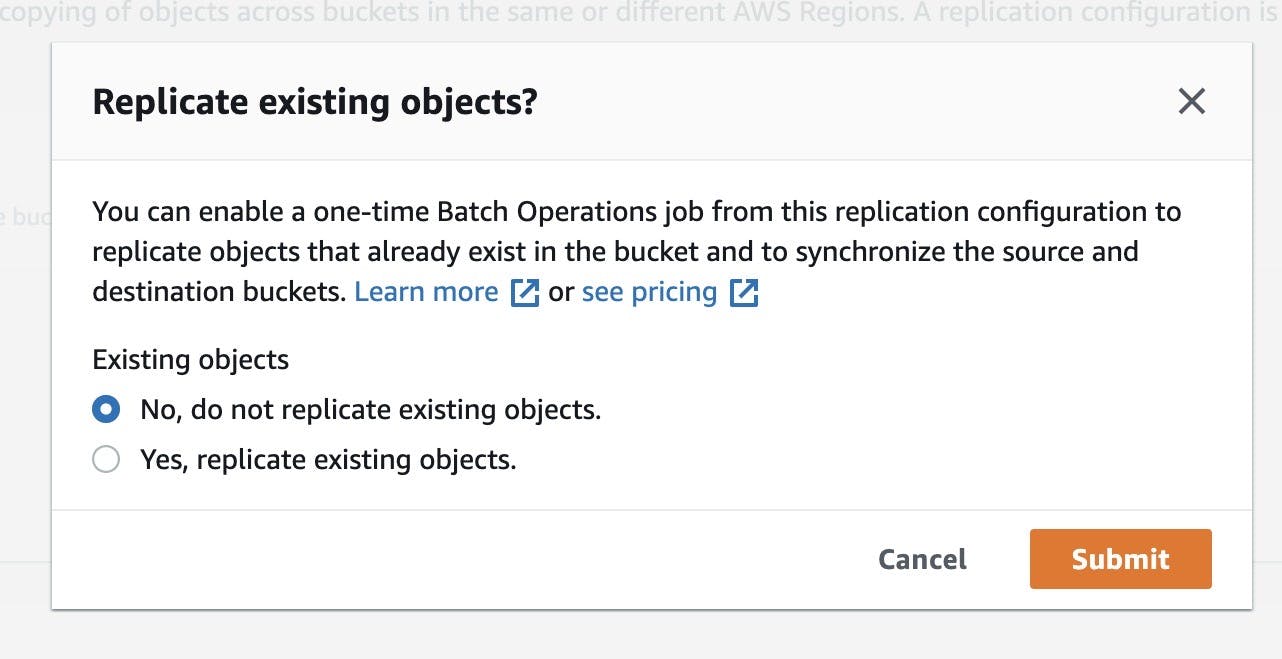
- AWS prompts if you want to replicate the existing objects in the bucket. For now, please select No and press to submit. We will cover the replication of existing objects in another tutorial.
- Once you create the replication rule, your configured rule will be visible under the Replication Rule with the status Enabled.
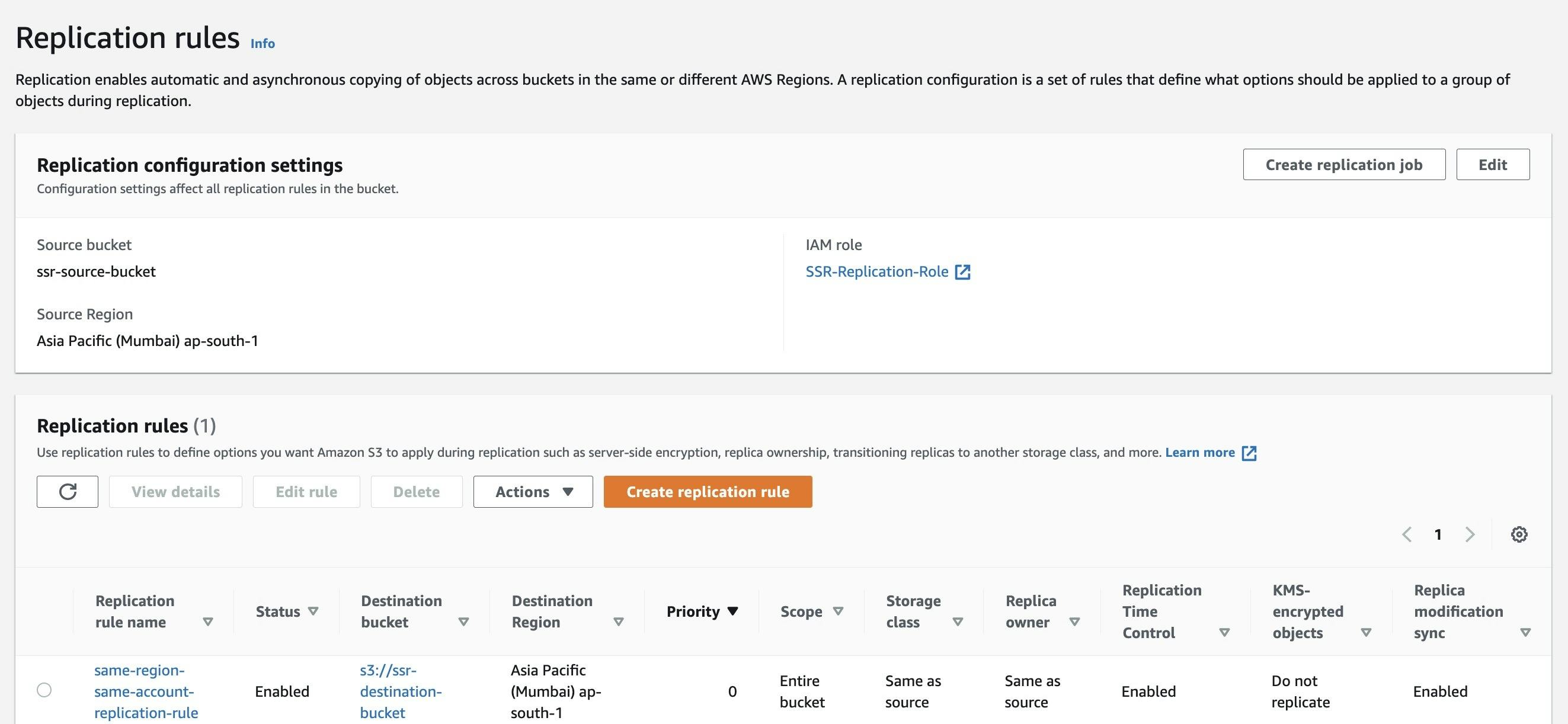
d. Test the S3 bucket Replication
- Now, it's time to test the replication. First, move to your source bucket and upload any file using the upload option.
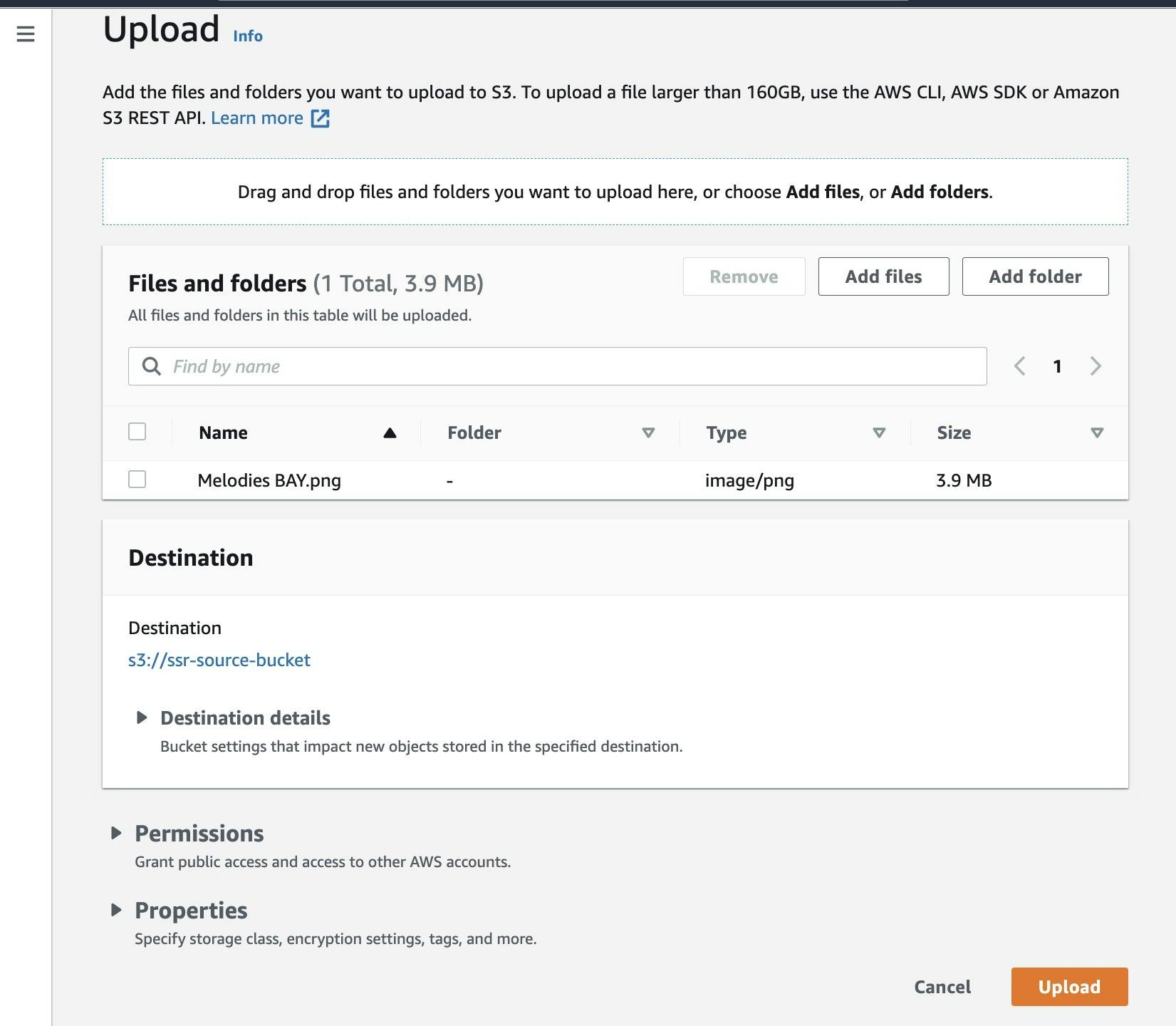
- Wait for a couple of minutes and check your destination bucket, where the Object from the source bucket is replicated and present in the destination bucket.
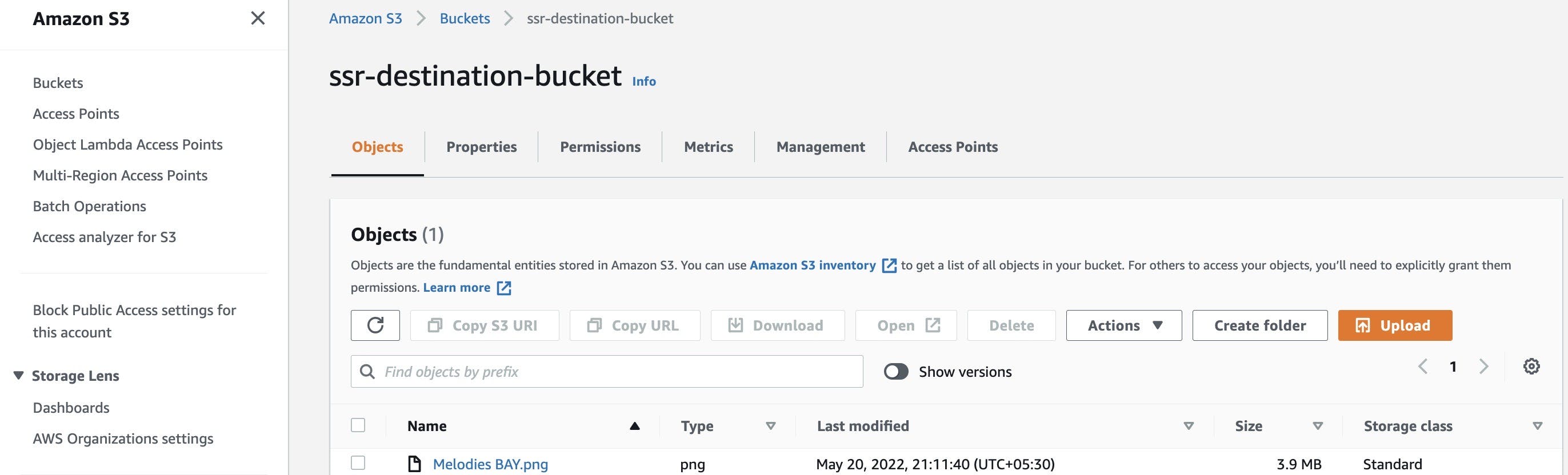
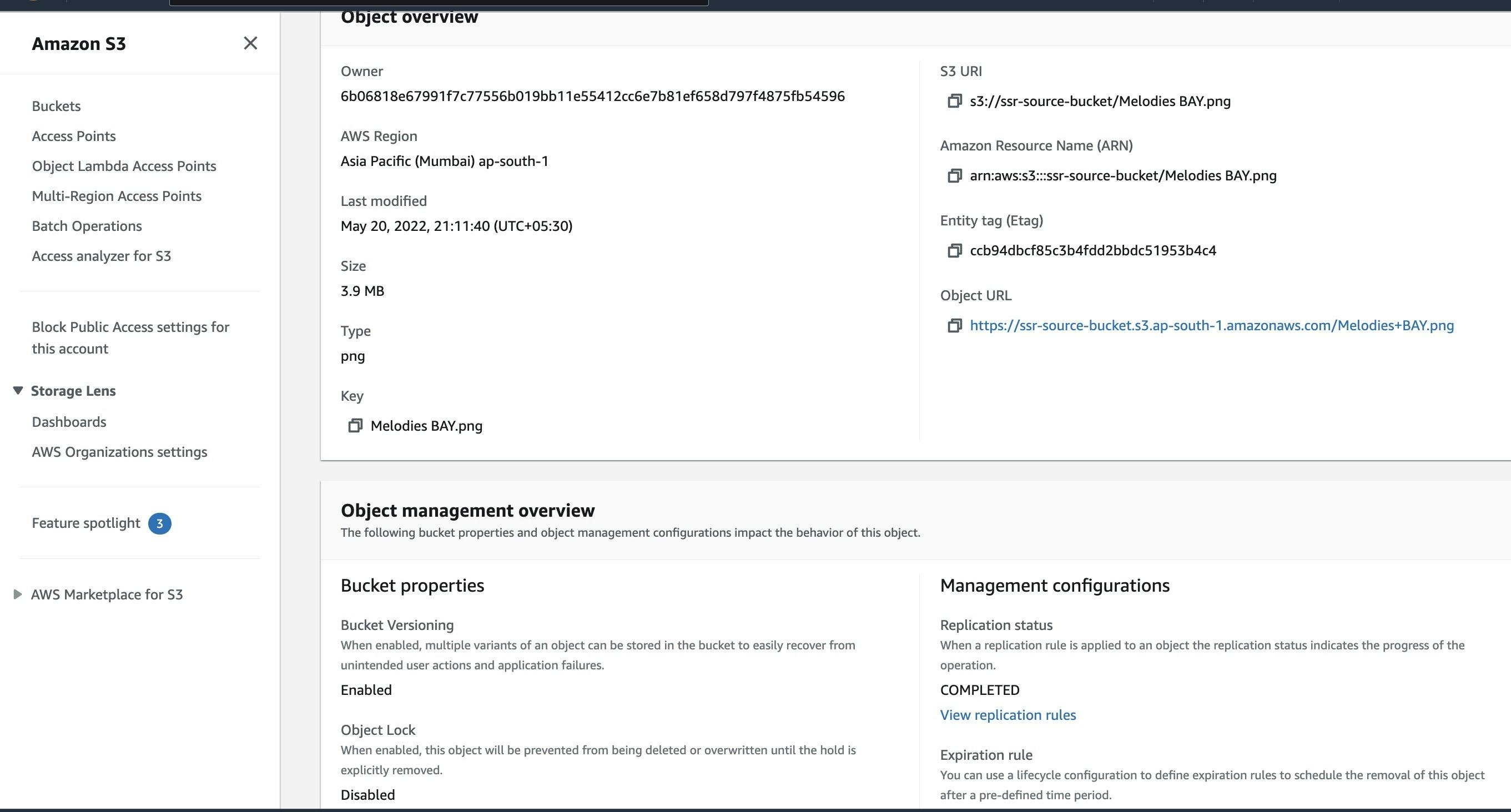
- You can also check the status of Object replication at the console.
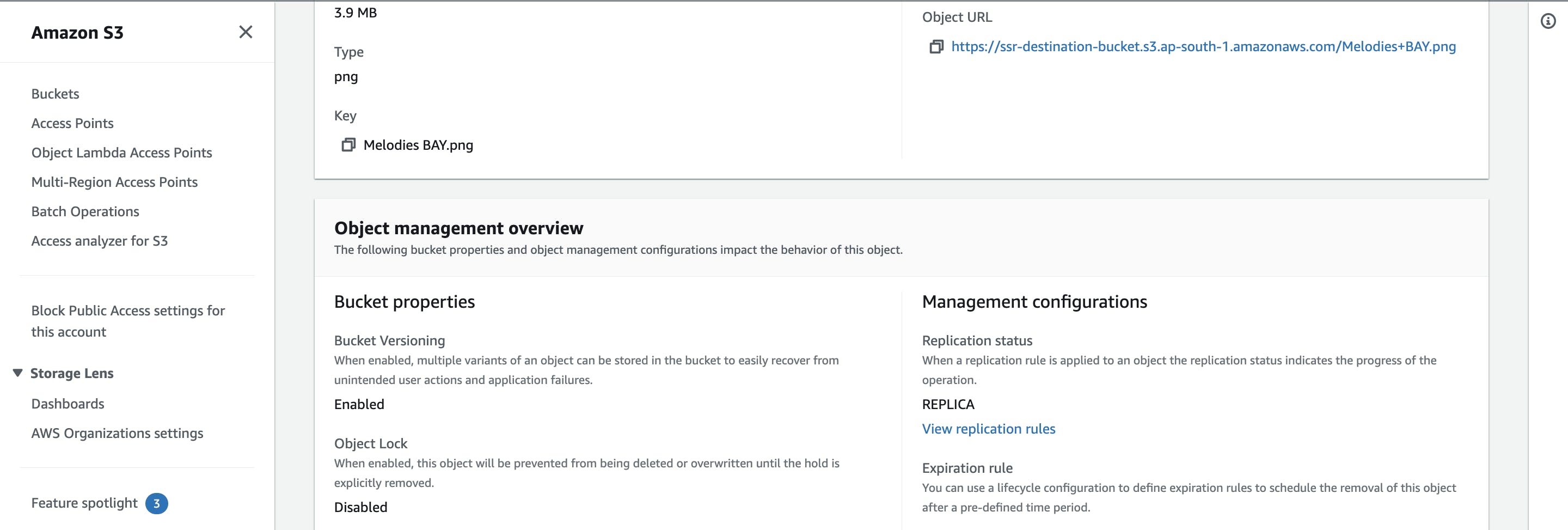
- Go source bucket and select the Object you uploaded
- Under the Object management overview, you can see the status of Replication as COMPLETED
AWS S3 Same Region Replication Pricing
For Same-Region Replication (SRR), the user needs to pay:
- For the S3 charges for storage in the selected destination S3 storage classes
- For Replication PUT requests
- For Infrequent Retrieval charges, if applicable
Conclusion
This article teaches you how to set up AWS S3 Same Region Replication easily and answers all your queries regarding it. Furthermore, it provides a brief introduction of various concepts related to it & helps the users understand them better and use them to perform data replication.
The related documents and files are present on Github URL
Feel free to provide your feedback and subscribe to our newsletter for upcoming posts.
To learn configure AWS S3 Cross Region Replication
Resources used:
To learn about AWS Lambda: